Template:SUIT-010
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
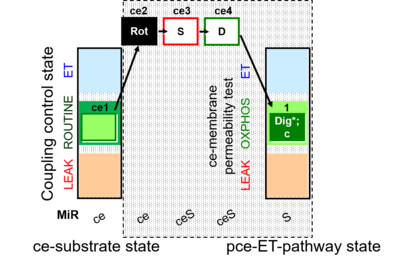
| ce2Rot | ROX | CII | ce1;ce2Rot
Succinate pathway control state (S-pathway) after inhibiting CI with rotenone, which also inhibits the F-pathway. | |
| ce3S | SL | S | CII | ce1;ce2Rot;ce3S
Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). Template:SUIT L n |
| ce4D | SP | S | CII | ce1;ce2Rot;ce3S;ce4D
Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |
| 1Dig | SP | S | CII | ce1;ce2Rot;ce3S;ce4D;1Dig
Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). Template:SUIT Digitonin titration OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |
| 1c | SP | S | CII | ce1;ce2Rot;ce3S;ce4D;1Dig;1c
Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). Addition of cytochrome c yields a test for integrity of the mtOM (cytochrome c control efficiency). Stimulation by added cytochrome c would indicate an injury of the mtOM and limitation of respiration in the preceding state without added c due to loss of cytochrome c. Typically, cytochrome c is added immediately after the earliest ADP-activation step (OXPHOS capacity P with saturating [ADP]). OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |