Difference between revisions of "SUIT-012"
From Bioblast
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
::: '''[[Categories of SUIT protocols |SUIT-category]]:''' N(PGM) | ::: '''[[Categories of SUIT protocols |SUIT-category]]:''' N(PGM) | ||
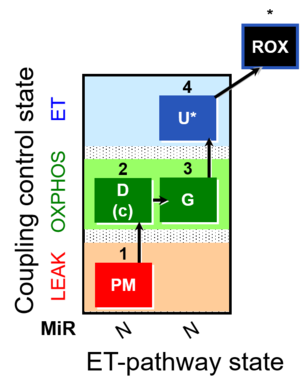
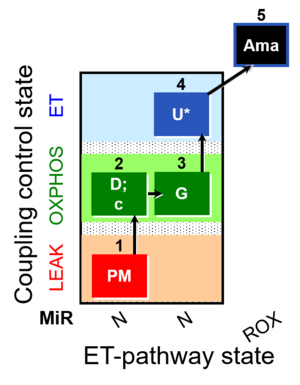
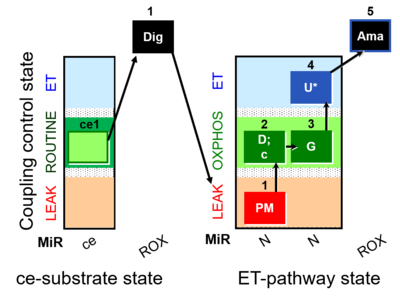
::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' diametral 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4U- | ::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' diametral 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4U- | ||
The SUIT-012 protocols specifically focus on assessing the linear coupling control ([[LEAK-respiration|''L'']]-[[Oxidative phosphorylation| ''P'']]-[[ET-capacity| ''E'']]) with NADH linked-substrates ([[PM pathway control state|PM]]) and the control in ET state ([[NADH_Electron_transfer-pathway_state|N]]). Addition of [[Glutamate|G]] in NADH-supported OXPHOS enables evaluating the [[glutamate anaplerotic pathway control state]]. SUIT-004 can be extended with the CIV assay module. | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
Communicated by [[Cardoso LH]], [[Doerrier C]], [[Huete-Ortega M]], [[Iglesias-Gonzalez J]] and [[Gnaiger E]] (last update 2019-01-28) | Communicated by [[Cardoso LH]], [[Doerrier C]], [[Huete-Ortega M]], [[Iglesias-Gonzalez J]] and [[Gnaiger E]] (last update 2019-01-28) | ||
Revision as of 11:00, 6 February 2019
Description
Abbreviation: N(PGM)
Reference: A ![]() »Versions
»Versions
- SUIT-category: N(PGM)
- SUIT protocol pattern: diametral 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4U-
The SUIT-012 protocols specifically focus on assessing the linear coupling control (L- P- E) with NADH linked-substrates (PM) and the control in ET state (N). Addition of G in NADH-supported OXPHOS enables evaluating the glutamate anaplerotic pathway control state. SUIT-004 can be extended with the CIV assay module.
Communicated by Cardoso LH, Doerrier C, Huete-Ortega M, Iglesias-Gonzalez J and Gnaiger E (last update 2019-01-28)
Specific SUIT protocols
- SUIT-012 O2 mt D027 for isolated mitochondria
- SUIT-012 O2 pce D### for permeabilized cells
References
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1PM | PML(n) | N | CI | 1PM
|
| 2D | PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2D
|
| 2c | PMcP | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c
|
| 3G | PGMP | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c;3G
|
| 4U | PGME | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4U
|
| 5Ama | ROX | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4U;5Ama
|
| Step | Respiratory state | Pathway control | ET-Complex | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ## AsTm | AsTmE | CIV | CIV | |
| ## Azd | CHB |
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary
Strengths and limitations
- + This protocol allows to evaluate the function of the TCA cycle without the involvement of the complex II (S-pathway). Would be useful to understand the contribution and the activity of the dehydrogenases.
- + Mitochondrial external membrane can be measured with the addition of cytochrome c. Application of the cytochrome c test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of c.
- + Reasonable duration of the experiment.
- + Complex IV activity can be measured.
- + GM and PM yield typically identical fluxes in human skeletal muscle fibres. However, PM is the superior alternative to GM: the fraction of the N-pathway is lower and of the S-pathway is higher with GM compared to PM (GMP is inhibited by the CII inhibitor malonic acid to a larger extent than PMP). PM, therefore, yields a more sensitive assay for the diagnosis of injuries in the N-pathway, since an impairment of N-pathway capacity can be compensated partially by activation of the S-pathway. This is an advantage compared to SUIT-011 for diagnosis of N-capacity.
- - Careful washing is required after the experiment to avoid carry-over of inhibitors and uncoupler.
Compare SUIT protocols
MitoPedia concepts: MiP concept, SUIT protocol, Recommended
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry