Difference between revisions of "Template:SUIT-003"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
| ce1;ce2Omy | | ce1;ce2Omy | ||
{{Template:SUIT L n}} | {{Template:SUIT L n}} | ||
*The addition of [[oligomycin]] or its carrier is optional depending on the experimental question to resolve. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 37: | Line 38: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 17:04, 18 January 2019
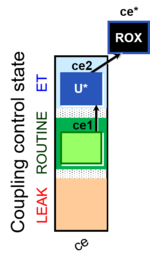
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M)
ROUTINE respiration in the physiological coupling state R. Externally added permeable substrates could contribute to this respiratory state. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ce2Omy | L | ce1;ce2Omy
| ||
| ce3U | E | ce1;ce2Omy;ce3U
Uncoupler titration (avoiding inhibition by high uncoupler concentrations) to obtain electron transfer (ET) capacity E (noncoupled ET-state). Test for limitation of OXPHOS capacity P by the phosphorylation system (ANT, ATP synthase, phosphate transporter) relative to ET capacity E in mt-preparations: E-P control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency. In living cells: E-R control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency. Noncoupled electron transfer state, ET state, with ET capacity E. | ||
| ce4Rot | ROX | ce1;ce2Omy;ce3U;ce4Rot
Succinate pathway control state (S-pathway) after inhibiting CI with rotenone, which also inhibits the F-pathway. Rox is the residual oxygen consumption in the ROX state, due to oxidative side reactions, estimated either after inhibition of CIII (e.g. antimycin A, myxothiazol), CIV (e.g. Cyanide) or in the absence of endogenous fuel-substrates. Rox is subtracted from oxygen flux as a baseline for all respiratory states, to obtain mitochondrial respiration. |