Difference between revisions of "SUIT-008"
From Bioblast
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
:::+ The presence of PGM and S establishes fully operative TCA cycle activity. | :::+ The presence of PGM and S establishes fully operative TCA cycle activity. | ||
:::+ This protocol allows to analyse the convergence of pathways at the Q-junction (N, NS, S). | :::+ This protocol allows to analyse the convergence of pathways at the Q-junction (N, NS, S). | ||
:::+ Mitochondrial external membrane can be measured with the addition of cytochrome c. Application of the cytochrome c test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of c. | :::+ Mitochondrial external membrane integrity can be measured with the addition of cytochrome c. Application of the cytochrome c test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of c. | ||
:::+ Reasonable duration of the experiment. | :::+ Reasonable duration of the experiment. | ||
:::+ Complex IV activity can be measured. | :::+ Complex IV activity can be measured. | ||
Revision as of 11:35, 6 February 2019
Description
Abbreviation: NS(PGM)
Reference: A ![]() »Versions
»Versions
- SUIT-category: NS(PGM)
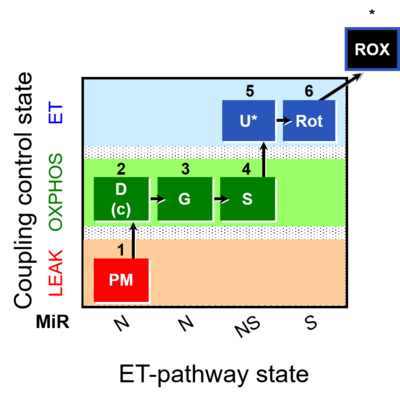
- SUIT protocol pattern: diametral 1PM;2D;3G;4S;5U;6Rot
The SUIT-008 protocols are designed to assess the linear coupling control (L- P- E) with NADH linked-substrates (PM) and the control in ET state (N, NS, S), covering the contribution of two pathways which are most important in the mitochondria of many species, tissues and cell types. With the addition of G in NADH-supported OXPHOS it enables evaluating the glutamate anaplerotic pathway control state. SUIT-004 can be extended with the CIV assay module.
Communicated by Cardoso LH, Doerrier C, Huete-Ortega M and Gnaiger E (last update 2019-01-28)
Specific SUIT protocols
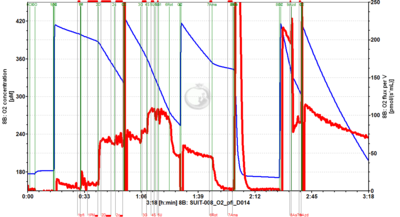
- SUIT-008 O2 pfi D014 for permeabilized fibers
- SUIT-008 O2 pce D025 for permeabilized cells
References
| Year | Reference | Organism | Tissue;cell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemieux 2017 Sci Rep | 2017 | Lemieux H, Blier PU, Gnaiger E (2017) Remodeling pathway control of mitochondrial respiratory capacity by temperature in mouse heart: electron flow through the Q-junction in permeabilized fibers. Sci Rep 7:2840. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-02789-8 | Mouse | Heart |
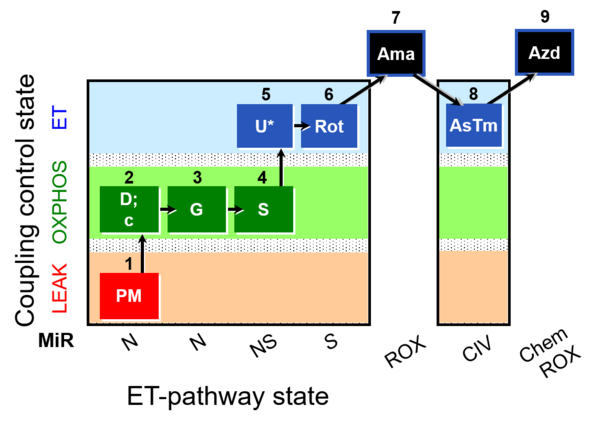
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1PM | PML(n) | N | CI | 1PM
|
| 2D | PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2D
|
| 2c | PMcP | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c
|
| 3G | PGMP | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c;3G
|
| 4S | PGMSP | NS | CI&II | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S
|
| 5U | PGMSE | NS | CI&II | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U
|
| 6Rot | SE | S | CII | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U;6Rot
|
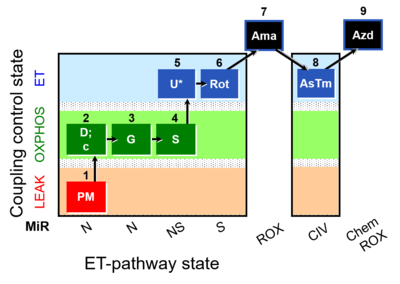
| 7Ama | ROX | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U;6Rot;7Ama
|
| Step | Respiratory state | Pathway control | ET-Complex | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ## AsTm | AsTmE | CIV | CIV | |
| ## Azd | CHB |
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary
Strengths and limitations
- + NS-OXPHOS capacity provides a physiologically relevant estimate of maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity.
- + The presence of PGM and S establishes fully operative TCA cycle activity.
- + This protocol allows to analyse the convergence of pathways at the Q-junction (N, NS, S).
- + Mitochondrial external membrane integrity can be measured with the addition of cytochrome c. Application of the cytochrome c test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of c.
- + Reasonable duration of the experiment.
- + Complex IV activity can be measured.
- + GM and PM yield typically identical fluxes in human skeletal muscle fibres. However, PM is the superior alternative to GM: the fraction of the N-pathway is lower and of the S-pathway is higher with GM compared to PM (GMP is inhibited by the CII inhibitor malonic acid to a larger extent than PMP). PM, therefore, yields a more sensitive assay for the diagnosis of injuries in the N-pathway, since an impairment of N-pathway capacity can be compensated partially by activation of the S-pathway. This is an advantage compared to SUIT-011 for diagnosis of N-capacity.
- - Fatty acid oxidation is not analysed.
- - When evaluating the additive effect of the N- and S-pathway, it has to be considered that NSP- and NSE-capacities can only be compared with NP- and SE-capacities. This is not a problem when NSP = NSE (Gnaiger 2009). In this case, it may be assumed that SP = SE (Votion et al 2012), such that NSP can be compared with NP + SP. SUIT-004 should be chosen for the additive effect in the ET-state.
- - Careful washing is required after the experiment to avoid carry-over of inhibitors and uncoupler.
Compare SUIT protocols
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
SUIT protocol,
Recommended
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry