Difference between revisions of "Template:Base quantities and count"
From Bioblast
| (37 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
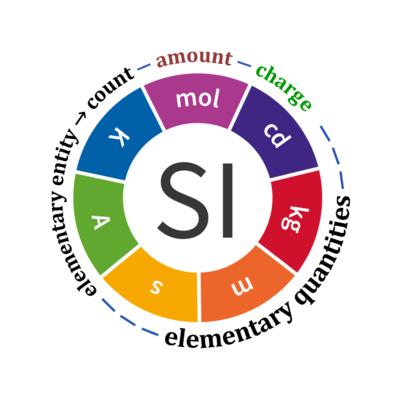
[[File:SI-units-elementary quantities.png|right|400px|link=Gnaiger 2020 MitoFit x]] | |||
::::: {| class="wikitable" | ::::: {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! Quantity !! Symbol for quantity ''Q'' !! Symbol for dimension !! Name of abstract unit ''u''<sub>''Q''</sub> !! Symbol for unit ''u''<sub>''Q''</sub> [*] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[elementary entity]] <sup>*,$</sup> || ''U''<sub>''X''</sub> || U || [[elementary unit]] || x | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[count]] <sup>*,$</sup> || ''N''<sub>''X''</sub> = ''N''·''U''<sub>''X''</sub> || X || [[elementary unit]] || x | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[amount]] of substance <sup>*,§</sup> || ''n''<sub>''X''</sub> = ''N''<sub>''X''</sub>·''N''<sub>A</sub><sup>-1</sup> || N || [[mole]] || mol | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Elementary charge |charge]] <sup>*,€</sup> || ''Q''<sub>el</sub> = ''z''<sub>''X''</sub>·''e''·''N''<sub>''X''</sub> || I·T || coulomb || C = A·s | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || || || || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ | | [[length]] || ''l'' || L || [[meter]] || m | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[mass]] || ''m'' || M || [[kilogram]] || kg | ||
|- | |- | ||
| luminous intensity || ''I''<sub>v</sub> || J || candela || cd | | time || ''t'' || T || [[second]] || s | ||
|- | |||
| electric current || ''I'' || I || [[ampere]] || A | |||
|- | |||
| thermodynamic temperature || ''T'' || Θ || [[kelvin]] || K | |||
|- | |||
| luminous intensity || ''I''<sub>v</sub> || J || [[candela]] || cd | |||
|} | |} | ||
:::: <sup>*</sup> For the quantities ''n'' and '' | ::::: [*] SI units, except for the canonical '[[elementary unit]]' [x]. The following footnotes are canonical comments, related to [[iconic symbols]]. | ||
:::: <sup> | ::::: <sup>*</sup> For the elementary quantities ''N''<sub>''X''</sub>, ''n''<sub>''X''</sub>, and ''Q''<sub>el</sub>, the entity-type ''X'' of the elementary entity ''U''<sub>''X''</sub> has to be specified in the text and indicated by a subscript: ''n''<sub>O<sub>2</sub></sub>; ''N''<sub>ce</sub>; ''Q''<sub>el</sub>. | ||
::::: <sup>$</sup> [[Count]] ''N''<sub>''X''</sub> equals the number of elementary entities ''U''<sub>''X''</sub>. In the SI, the quantity 'count' is explicitly considered as an exception: "Each of the seven base quantities used in the SI is regarded as having its own dimension. .. All other quantities, with the exception of [[count]]s, are derived quantities" ([[Bureau International des Poids et Mesures 2019 The International System of Units (SI)]]). An elementary entity ''U''<sub>''X''</sub> is a material unit, it is not a count (''U''<sub>''X''</sub> is not a number of ''U''<sub>''X''</sub>). ''N''<sub>''X''</sub> has the dimension X of a count and ''U''<sub>''X''</sub> has the dimension U of an elementary entity; both quantities have the same abstract unit, the 'elementary unit' [x]. | |||
::::: <sup>§</sup> [[Amount]] ''n''<sub>''X''</sub> is an elementary quantity, converting the elementary unit [x] into the [[SI base units |SI base unit]] mole [mol] using the [[Avogadro constant]] ''N''<sub>A</sub>. | |||
::::: <sup>€</sup> [[Charge]] is a derived SI quantity. Charge is an elementary quantity, converting the elementary unit [x] into coulombs [C] using the [[elementary charge]] ''e'', or converting moles [mol] into coulombs [C] using the [[Faraday constant]] ''F''. ''z''<sub>''X''</sub> is the charge number per elementary entity ''U''<sub>''X''</sub>, which is a constant for any defined elementary entity ''U''<sub>''X''</sub>. ''Q''<sub>el</sub> = ''z''<sub>''X''</sub>·''F''·''n''<sub>''X''</sub> | |||
Latest revision as of 08:02, 6 July 2023
Quantity Symbol for quantity Q Symbol for dimension Name of abstract unit uQ Symbol for unit uQ [*] elementary entity *,$ UX U elementary unit x count *,$ NX = N·UX X elementary unit x amount of substance *,§ nX = NX·NA-1 N mole mol charge *,€ Qel = zX·e·NX I·T coulomb C = A·s length l L meter m mass m M kilogram kg time t T second s electric current I I ampere A thermodynamic temperature T Θ kelvin K luminous intensity Iv J candela cd
- [*] SI units, except for the canonical 'elementary unit' [x]. The following footnotes are canonical comments, related to iconic symbols.
- * For the elementary quantities NX, nX, and Qel, the entity-type X of the elementary entity UX has to be specified in the text and indicated by a subscript: nO2; Nce; Qel.
- $ Count NX equals the number of elementary entities UX. In the SI, the quantity 'count' is explicitly considered as an exception: "Each of the seven base quantities used in the SI is regarded as having its own dimension. .. All other quantities, with the exception of counts, are derived quantities" (Bureau International des Poids et Mesures 2019 The International System of Units (SI)). An elementary entity UX is a material unit, it is not a count (UX is not a number of UX). NX has the dimension X of a count and UX has the dimension U of an elementary entity; both quantities have the same abstract unit, the 'elementary unit' [x].
- § Amount nX is an elementary quantity, converting the elementary unit [x] into the SI base unit mole [mol] using the Avogadro constant NA.
- € Charge is a derived SI quantity. Charge is an elementary quantity, converting the elementary unit [x] into coulombs [C] using the elementary charge e, or converting moles [mol] into coulombs [C] using the Faraday constant F. zX is the charge number per elementary entity UX, which is a constant for any defined elementary entity UX. Qel = zX·F·nX